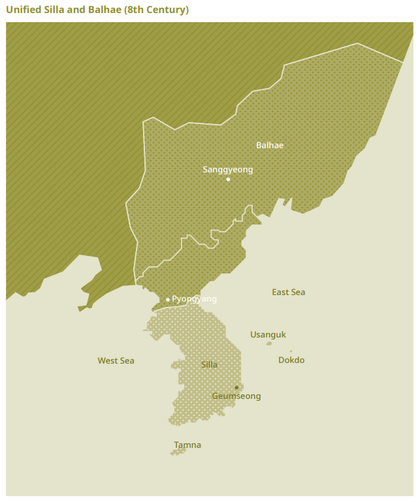
Northern and Southern States Period: Unified Silla and Balhae
Northern and Southern States Period: Unified Silla and Balhae
With the unification of the three Kingdoms on the Korean Peninsula in 668, Silla enjoyed a marked expansion of both its territory and population. Unified Silla entered a period of dazzling economic development. It mended fences with Tang China. The two countries saw vigorous exchanges between traders, monks, and Confucian scholars. Silla exported gold and silver handiworks and ginseng to Tang and imported books, ceramic ware, satin silk fabric, clothes, and craftwork products. Goods from Central Asia were introduced to Silla, and traders from that region paid visits to Silla via the Silk Road and sea routes.
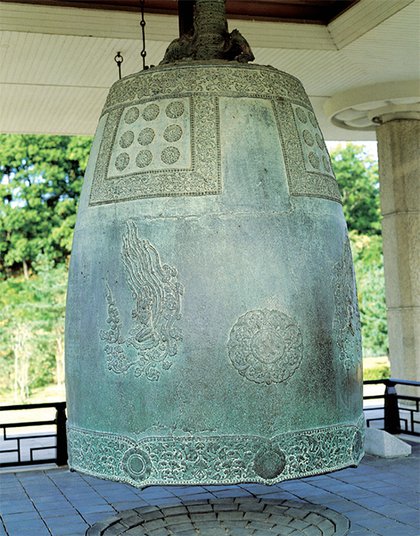


- Sacred Bell of Great King Seongdeok (Unified Silla; 8th Century): Weighing 18.9 tons, this is the largest bell in the country. It is also called the Emille Bell. The Flying Apsaras in the picture on the right displays the exquisite decorative skills of Silla.
The major ports of Silla included Ulsan and Danghangseong (present-day Hwaseong, Gyeonggi-do), through which numerous goods from Central and Southern Asia were imported. In the early 9th century, General Jang Bo-go of Silla established a forward base in Cheonghaejin (present-day Wando, Jeollanamdo) to deal with the pirate menace and encourage trade with nearby countries including China and Japan.
In the meantime, the survivors of the fallen Kingdom of Goguryeo resisted Tang China’s rule. In 698, a group of them led by Dae Jo-yeong, jointly with the Mohe, founded Balhae near present-day Dongmiaoshan in Jilin province, China. The new Kingdom would eventually confront Silla in the south.
Balhae started expanding its territory and regained control over most of the former territory of Goguryeo. During the reign of King Mu, Balhae controlled the northern parts of Manchuria. King Mun reformed the system of governance and moved the capital to Sanggyeong (present-day Ningan-xian, Heilongjiang province) in about 755. The people of Balhae took pride in their Goguryeo inheritance. Letters held in Japan show that the kings of Balhae referred to themselves as the Kings of Goguryeo. Balhae eventually grew so large and strong that the people of Tang China called it Haedong Seongguk (“prosperous country in the east”), but it fell in 926 as a result of an eruption of Baekdusan Mountain and an invasion of the Khitan people.
